Scientific Objectives
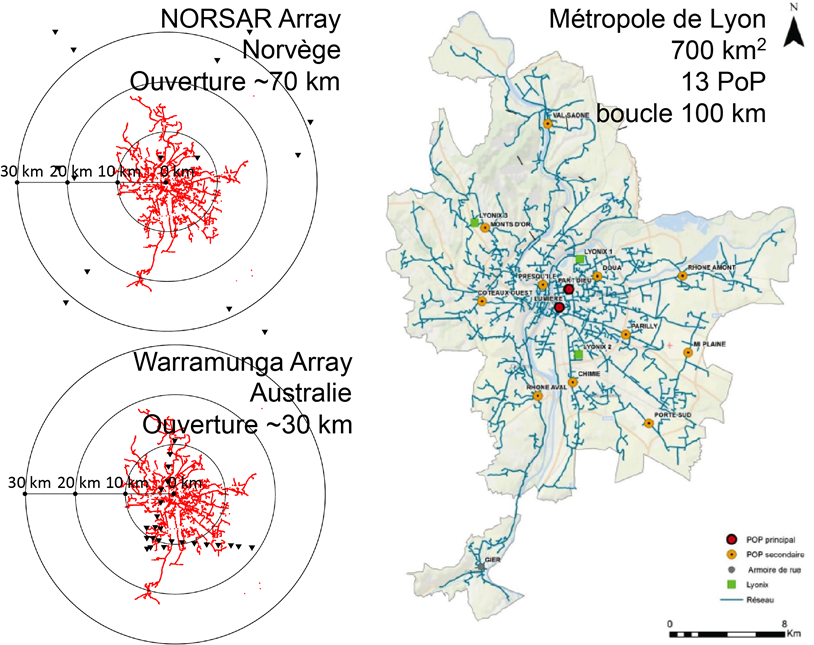
By leveraging modern seismology techniques, experts can detect micrometer-scale ground motions for urban seismic noise analysis, soil characterization, hydrological cycle study, infrastructure design, and seismic risk reduction. This process involves precise measurements of ground motions with point-wise seismic sensors, and interpreting this data after interpolation. DASARA aims to convert urban fiber optic networks into high-density seismic antennas providing coverage comparable to modern antennas while allowing for considerably higher spatial resolution (Figure 1).
This initiative, using the Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technique on fiber optic cables, is tested on the commercial fiber optic network in Lyon Metropole area. It successfully gathered exploitable geophysical data and now aims to develop a comprehensive monitoring system for this network. Analytical and numerical processing tools are being developed and experimentally validated through partnerships with various local entities. These tools facilitate the acquisition, storage, and analysis of massive data generated by DAS, producing useful maps to analyze urban seismic noise, human mobility, and interactions between soils and structures, thus promoting the creation of resilient cities against anthropic vibrations and earthquakes.
The roadmap of the project
Scientific Tools for Assessing Seismic Noise in the Environment
The DASARA project aims to provide a comprehensive and generic framework dedicated to the collection, modeling, and assessment of vibrations in the environment using telecommunication optical networks. This project is divided into two modules: the measurement module, and the spatial data infrastructure module.